https://practice.geeksforgeeks.org/problems/inorder-successor-in-bst/1
In Binary Tree, Inorder successor of a node is the next node in Inorder traversal of the Binary Tree. Inorder Successor is NULL for the last node in Inoorder traversal.
In Binary Search Tree, Inorder Successor of an input node can also be defined as the node with the smallest key greater than the key of input node. So, it is sometimes important to find next node in sorted order.
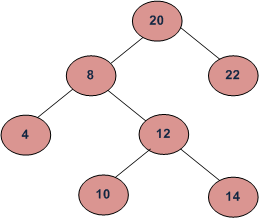
In the above diagram, inorder successor of 8 is 10, inorder successor of 10 is 12 and inorder successor of 14 is 20.
給你BST樹中的任一node,請return它在inorder中的下一個node。
[思路]
假設你已經會基本的inorder traverse。那麼應該不難理解一個node的successor只有兩種case:
1.我的右子樹中的最左下角的值(BST中的最小值)。也就是先向right child走,然後向左一路走到底,就是successor。例如8的successor是10。
2.若沒有右子樹,那就是我與祖先們中的第一個"left child"的爸爸。也就是檢查我是不是left child,我爸是不是left child,我爸的爸是不是left child...。找到第一個left child,此人的爸爸就是successor。例如14的successor是20。
所以假設TreeNode structure中有pointer to parent,那麼很容易就可以完成這題。
struct Node{
Node* right;
Node* left;
Node* parent;
int val;
Node(int v):val(v){};
};
class Solution {
public:
Node* inorderSuccessor(Node *curnode) {
if (curnode==NULL) return NULL;//error handling
if (curnode->right) {
Node *c = curnode->right;
while (c->left)
c = c->left;
return c;
} else {
Node *me = curnode, *myfather = me->parent;
while (me && myfather && myfather->left != me) {
me = myfather;
myfather = myfather->parent;
}
return myfather;
}
}
};
[進階題思路]
要是TreeNode中沒有pointer to parent怎麼辦? 這樣我完全無法單純透過自己找到祖先的資訊。沒錯 ! 因此需要從root找起。
概念和上面一樣分兩個case:
1.我的右子樹中的最左下角的值。...同上
2.若沒有右子樹,就從root開始尋找我,在尋找的路途中,"最後的left child"的爸爸,就是successor。例如尋找14的過程中,最後的left child是8, 因此successor是8的爸爸20。
概念和上面一樣分兩個case:
1.我的右子樹中的最左下角的值。...同上
2.若沒有右子樹,就從root開始尋找我,在尋找的路途中,"最後的left child"的爸爸,就是successor。例如尋找14的過程中,最後的left child是8, 因此successor是8的爸爸20。
/*The structure of Node
struct Node {
int data;
Node * right, * left;
};*/
/* The below function should return the node which is
inorder successor of given node x. */
Node * inOrderSuccessor(Node *root, Node *x)
{
if(!x) return NULL;
//Your code here
if(x->right){
x=x->right;
while(x->left!=NULL)
x=x->left;
return x;
}
if(!root) return NULL;
Node* succ=NULL;
while(root && root->data!=x->data){
if(root->data < x->data){
root=root->right;
}
else if(x->data < root->data)
{
succ=root;
root=root->left;
}
}
return succ;
}